Sickle Cell Anemia — Symptoms, Treatment, and What to Watch For
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic blood disorder that changes red blood cells into a C shape. That twist makes them sticky and rigid, so they block small blood vessels. The result is sudden, severe pain (pain crises), low oxygen to organs, and higher infection risk. Around 100,000 people in the United States live with sickle cell disease, and millions more worldwide carry variants. If you or a family member has sickle cell, practical daily steps make a big difference.
Quick signs to watch for include ongoing fatigue, shortness of breath, yellowing of the eyes, frequent infections, and sudden episodes of sharp limb or chest pain. Children often show jaundice and delayed growth. Lab tests show low hemoglobin and a high number of abnormal red cells. Newborn screening catches most cases early, which gives a big advantage for preventing complications.
Treatment and everyday care
Hydroxyurea (Hydrea) is a common medicine that reduces pain crises and the need for transfusions. It needs regular blood tests to watch the bone marrow and adjust doses. If you read our Hydrea article, you'll find tips on spotting side effects and when to call your doctor. Blood transfusions help during severe anemia or stroke risk; specialists manage frequency and iron overload. Curative options include bone marrow or stem cell transplant, but they carry risks and need a matched donor.
Vaccines, antibiotics for young children, and prompt treatment of fevers lower infection danger. Avoiding dehydration, extreme temperatures, and high altitude can reduce crises. Pain management plans, approved opioid use for severe attacks, and non-opioid strategies for steady home care are part of a smart plan. Work with a hematologist who knows sickle cell; they'll help set up routine labs, imaging, and a personalized action plan.
Living with sickle cell and planning ahead
Think about genetic counseling before having children - sickle cell trait can be passed even by symptom-free parents. Track your crisis triggers and symptoms in a simple diary to share with your care team. Mental health matters: chronic pain and hospital stays add stress, so find support groups or counseling early. If you travel, carry a letter from your doctor, a recent lab summary, and a plan for managing pain or transfusion needs.
Emergency signals that need immediate care include sudden weakness or numbness, slurred speech, high fever, severe chest pain, or trouble breathing. These can mean stroke, severe infection, or lung problems that need urgent treatment. With regular care, vaccination, and a clear plan, many people with sickle cell live active lives. Use trusted sources and specialists to guide treatment choices and check our related posts for practical drug and care guides.
If you're looking for drug info, read our Hydrea side effects article and other posts about antibiotics, transfusion care, and travel advice. Ask your pharmacist about vaccine timing and iron chelation if transfusions are frequent. Small steps now prevent big problems later - keep records, ask questions, and stay connected to care starting today.
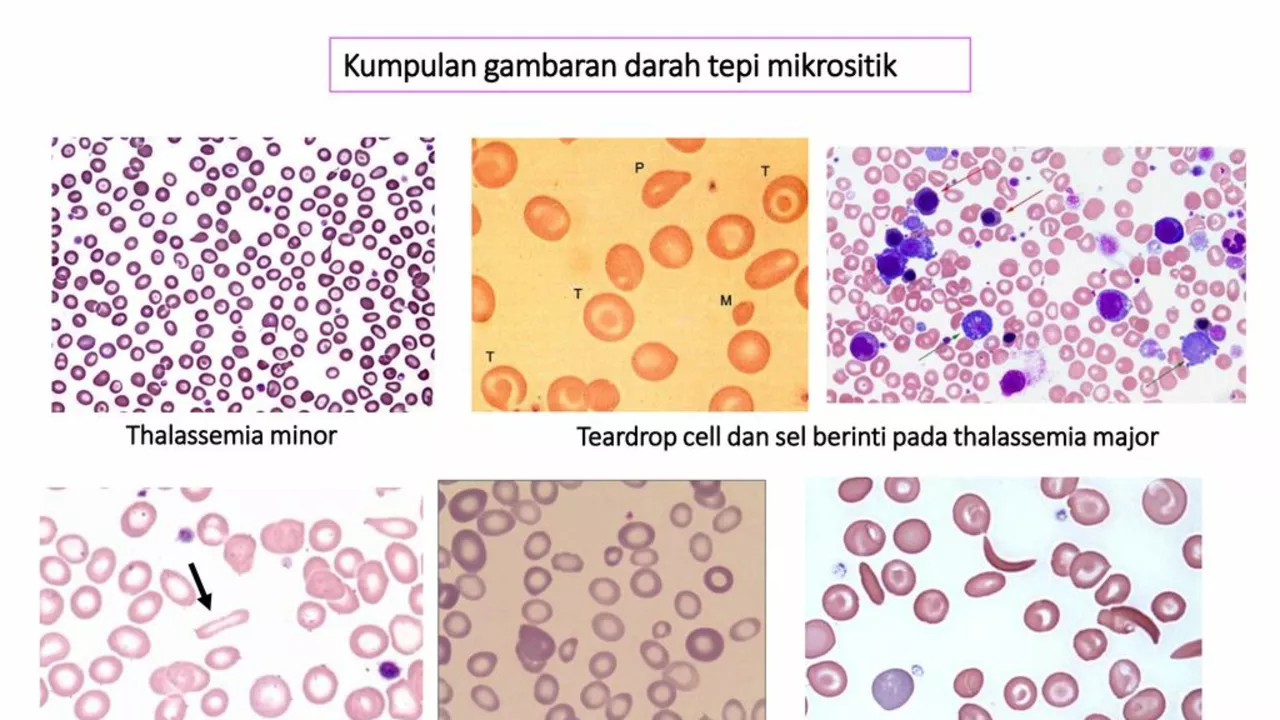
The Importance of Early Diagnosis in Sickle Cell Anemia
In my recent exploration, I've come to understand the immense importance of early diagnosis in sickle cell anemia. This disease, caused by an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein hemoglobin, can lead to a life of pain and complications if not detected early. Early diagnosis provides a chance for proper management of the disease, reducing potential crises and extending life expectancy. Additionally, it allows for informed family planning, as sickle cell is a hereditary disease. Remember, the sooner the diagnosis, the better the chances for a healthier life.
Read More